Blog - Source Code Management, Tools, and Best Methods in 2024
Prior to the introduction of source code management, developers relied on manual notifications to coordinate their work on files, risking simultaneous edits and lacking a comprehensive record of changes. This approach was unreliable and hindered bug tracing efforts. Source code management addresses these issues by systematically tracking alterations, preventing accidental overwrites, and flagging conflicts. As a result, developers can effectively resolve conflicts before integrating changes into the codebase, enhancing the overall quality of the application.
This article delves into the intricacies of source code management, examining its definition, advantages, significance, available tools, and recommended practices. Whether you’re a seasoned programmer, a tech aficionado, a novice, or somewhere in between, this comprehensive guide addresses all your queries regarding source code management.
What is source code?

Source code comprises human-readable instructions written in a programming language, forming the basis for developing computer software and applications.
In simpler terms, it refers to programming statements crafted by a programmer using a text editor or visual programming tool, then stored in a file. It serves as a critical component of a computer program, typically consisting of functions, definitions, calls, methods, and other operational statements.
In the 1940s, the earliest software was written in binary code. An early example of recognizable source code dates back to Tom Kilburn, a pioneer in computer science. In 1948, Kilburn achieved a milestone by creating the first digital program stored electronically in a computer’s memory, which solved a mathematical equation.
In essence, programmers use programming languages like C++, Python, Java, etc., to articulate instructions using words, symbols, and structures akin to natural language. These instructions are then translated into machine-readable code that computers can execute. This set of instructions, authored by the programmer, constitutes the source code.
In the context of software projects, the source code emerges as a paramount asset, serving as the foundation for the entire application.
How are codes written in source code?
Typically, source code is crafted to be easily understood by developers, programmers, and other users.
For instance, let’s take a basic JavaScript program that prints “Hello World!” to the console.
Someone without programming experience can still interpret the purpose of this program—it’s meant to display “Hello World!” in the console. However, for the computer’s processor to execute these instructions, the source code must first be translated into machine language. This conversion is facilitated by a specific interpreter program called a compiler. Once compiled, the source code transforms into object code.
What are the types of source code?
Source code can be classified into various types based on the programming languages or technologies employed. Here are some common categories:
- 1. Procedural Source Code: This type follows a procedural programming approach, where instructions are executed sequentially to achieve a specific outcome.
- 2. Object-Oriented Source Code: Based on object-oriented programming (OOP) principles, this type utilizes classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, and encapsulation to organize and structure the code effectively.
- 3. Scripting Source Code: Scripting languages like JavaScript, Python, or Ruby are used to write scripts, typically interpreted at runtime. They are commonly employed for tasks such as automation, system administration, and web development.
- 4. Markup Source Code: Employed in markup languages like HTML and XML, this type defines the structure, formatting, and presentation of data on web pages or in documents.
- 5. Compiled Source Code: Languages like C, C++, Java, or Swift require source code to be compiled into machine-readable instructions before execution by the computer’s processor.
- 6. Functional Source Code: Functional programming languages such as Haskell or Lisp involve writing functional source code, emphasizing the use of pure functions and immutable data.
- 7. Database Source Code: Database-specific languages like SQL (Structured Query Language) are used to write database source code, defining and manipulating database structures, queries, and data.
These are just a few examples of source code types. The choice of source code type depends on factors like the programming language, technology, or domain being worked on.
Is the source code considered intellectual property?
While source code is frequently governed by intellectual property laws like copyright and licensing, programmers have the option to release their code under open-source licenses. This grants other programmers the freedom to use, modify, and distribute the code without restrictions. Alternatively, programmers may opt to keep their code proprietary, thereby limiting others from using or modifying it without explicit permission. However, this aspect is not the central focus of this article.
What is source code management?

Source code management encompasses the efficient and methodical process of monitoring and governing changes applied to a software project’s source code throughout its entire development journey.
Put simply, it refers to the systematic tracking of alterations made to a source code repository.
A source code repository serves as a hub for storing not just code but also various assets crucial to software development, such as documentation, tests, and scripts. It acts as a central point for managing and structuring a project’s codebase, enabling collaboration among developers. Often referred to as a central server housing an organization’s complete codebase, it is governed by a source code management system, overseeing code modifications across different development projects.
Maintaining a comprehensive history of code changes is instrumental for programmers, developers, and testers to ensure they consistently work with up-to-date and accurate code. Moreover, it facilitates the resolution of conflicts that may arise during the integration of code from diverse sources.
Among its numerous advantages, source code management systems facilitate smoother collaboration among programmers, mitigating the risk of inadvertent overwriting of each other’s work. Source code management is frequently used synonymously with version control.
What are source code management core concepts?
Source code management (SCM) centers on effectively managing and overseeing changes to source code files. Here are key concepts that underscore SCM:
- Version Control: This empowers developers to monitor various versions of their source code files. It permits independent changes, facilitates reverting to previous versions, and merges modifications from different sources seamlessly.
- Repository: Think of a repository as a designated storage area for all source code files. It resembles an orderly warehouse accessible only to authorized team members. It maintains a comprehensive history of the codebase, allowing easy reference to previous versions.
- Branching and Merging: Developers can create branches for working on features or experiments, akin to distinct development paths. This enables concurrent work without impacting the main codebase. Merging branches consolidates changes into the codebase when ready.
- Change Tracking: Version control systems meticulously log every alteration made to source code files. They document details like the author, timestamp, and specific modifications, aiding in issue identification, understanding code evolution, and reverting when necessary.
- Collaboration: Version control systems facilitate developer collaboration, offering mechanisms for concurrent work on the codebase. They also assist in conflict resolution when multiple developers modify the same code simultaneously, fostering overall coordination.
These foundational concepts are pivotal in source code management, enabling developers to operate efficiently, uphold code integrity, and monitor the codebase’s progression over time.
Tools and software for managing source code
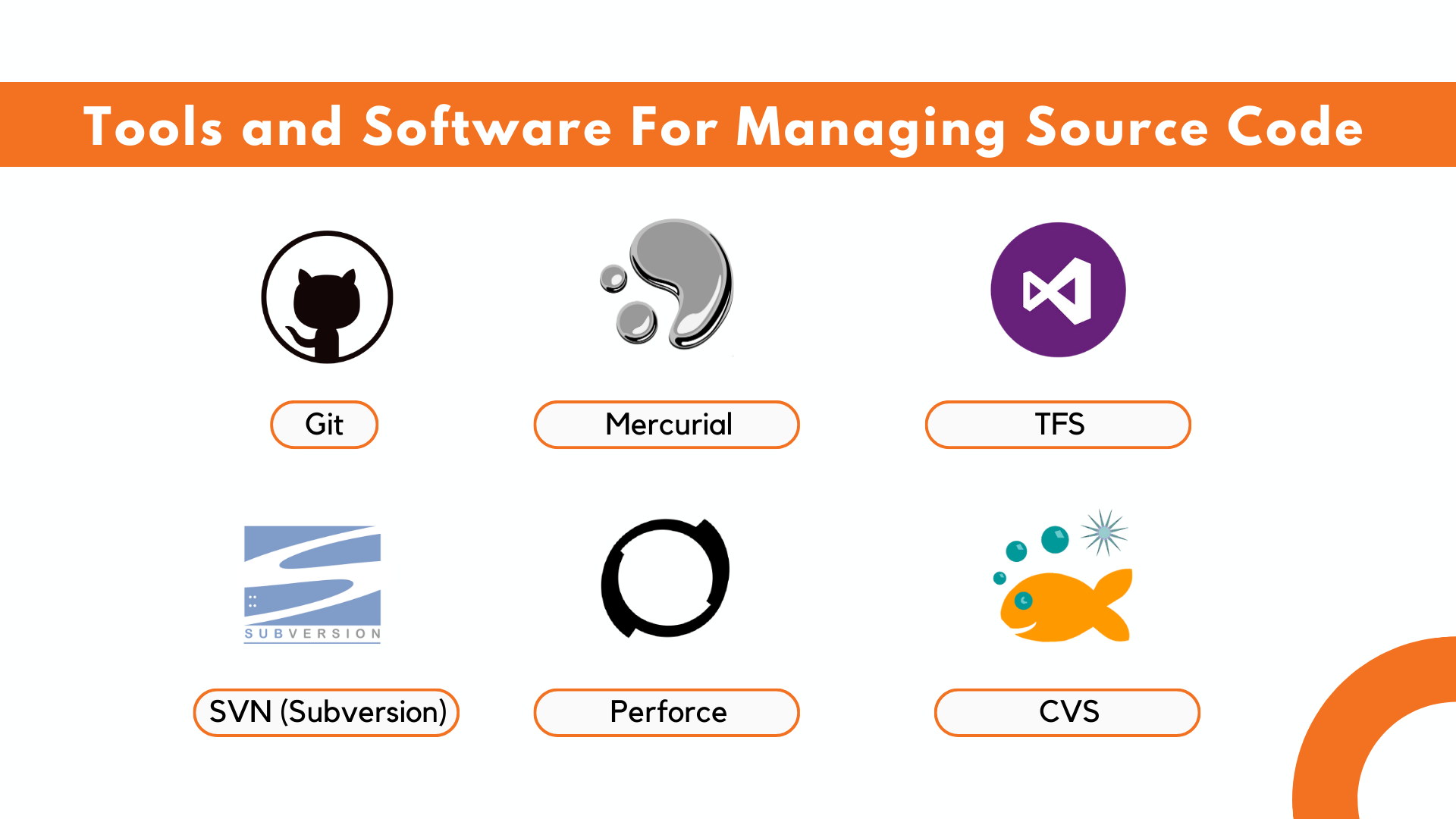
Besides its human-readable format, source code is also machine-processable, enabling various tools and applications to analyze and manipulate it. These tools assist developers in identifying errors or inefficiencies, automating testing, and optimizing the development process.
A multitude of software and tools cater to source code management. Here are several popular choices:
- Git: Git is a distributed version control system adept at tracking changes in source code during software development.
- SVN (Subversion): SVN serves as a centralized version control system for managing and monitoring changes in source code files.
- Mercurial: Mercurial is a distributed version control system specifically crafted for software development endeavors.
- Perforce: Perforce operates as a centralized version control system, offering robust performance and scalability for large-scale projects.
- TFS (Team Foundation Server): TFS is a centralized version control system seamlessly integrating with various Microsoft development tools.
- CVS (Concurrent Versions System): CVS, an enduring centralized version control system, is still utilized in some legacy projects.
Moreover, there exist web-based hosting platforms like Bitbucket, GitHub, and GitLab, furnishing collaboration and version control capabilities. When selecting a source code management tool or software, it’s crucial to assess the project’s and team’s unique requirements to ensure compatibility and efficacy.
How does source code management differ from version control?
The terms “source code management” and “version control” are frequently used interchangeably, both referring to the process, practices, and tools employed to oversee and regulate changes made to source code files.
However, when distinguishing between them, we can view “version control” as a specific aspect or subset of “source code management.”
Version control primarily concerns the management of different iterations of code, facilitating the tracking of changes, rollback to prior versions, and integration of modifications from various developers into the codebase.
In contrast, “source code management” encompasses a broader spectrum, incorporating version control while extending to additional facets such as repository administration, collaborative utilities, code structuring, and workflow management. Source code management systems typically offer functionalities beyond version control, including issue tracking, code review capabilities, continuous integration, and automated deployment.
In essence, although often used interchangeably, “source code management” embodies a more comprehensive concept that incorporates version control as just one element among its various components.
How does source code management differ from source control management?
“Source code management” and “source control management” are essentially synonymous terms often used interchangeably to describe the practice of overseeing and regulating changes made to source code files.
Despite slight differences in wording, both terms carry the same underlying meaning. They encompass the process and tools utilized for tracking, organizing, and collaborating on source code within software development projects. Both concepts encompass version control, repository management, collaboration functionalities, and the monitoring and governance of changes to the source code.
In essence, “source code management” and “source control management” denote the same practice and tools employed to manage and control source code files.
Why is source code management important?
Tracking modifications to source code is a vital practice, and source code management offers a variety of valuable features to enhance collaborative code development. Here are some reasons why source code management is crucial:
- Detailed Historical Record: Source code management meticulously records the project’s lifecycle from inception, allowing for comprehensive historical documentation. This record facilitates the undoing of changes to the codebase when necessary, empowering developers to revert to previous states effortlessly. This feature is invaluable in preventing regressions during updates, showcasing the remarkable capability of source code management to rectify mistakes without compromising the codebase’s integrity.
- Code Backup: By centralizing code storage, source code management ensures universal accessibility and facilitates convenient backups. Unlike storing code on individual devices, which poses risks such as theft or crashes, centralized storage minimizes the likelihood of data loss. Additionally, backing up code becomes more manageable and efficient under this centralized arrangement.
- Seamless and Effective Communication: Source code management platforms often include chat interfaces, enabling developers to comment, ask questions, and discuss code changes within the workflow. This fosters enhanced communication among team members, management, and users, particularly beneficial for geographically dispersed teams.
- Smooth Collaboration: Collaboration is integral to most software projects, and source code management streamlines this process. Developers can work on different sections of code simultaneously in their respective workspaces without the fear of conflicting changes. The system alerts developers to potential conflicts arising from isolated code alterations, providing an opportunity for review and resolution before integrating changes. Moreover, the capability to revert to previous states in case of merged code conflicts ensures code stability and maintains collaboration efficiency.
Recommendations and Best Practices for Source Code Management
After acknowledging the benefits of source code management and its importance, here are some recommended practices and guidelines to effectively utilize source code management:
- 1. Clear and Concise Commit Messages: Ensure commit messages are succinct yet descriptive, aiding team members in comprehending changes and facilitating seamless tracking of development progress.
- 2. Utilization of Branching Strategies: Employ branching strategies to enable concurrent work on different versions of the codebase. Choose a strategy like Gitflow, Feature Branching, or Trunk-Based Development that aligns with the project and team requirements.
- 3. Regular Code Reviews: Conduct frequent code reviews to detect errors, identify potential issues, foster knowledge sharing among team members, and enhance overall code quality and development efficiency.
- 4. Automation Tools Integration: Implement automation tools to streamline repetitive tasks like testing and deployment, saving time and minimizing errors. SCM tools such as Jenkins, Travis CI, and CircleCI can automate various stages of the development process, enhancing efficiency.
- 5. Maintain a Clean Repository: Ensure the repository remains organized and clutter-free, facilitating easy navigation and collaboration among team members. Keep the repository tidy by eliminating unnecessary files and avoiding duplicate code.
By adhering to these recommended practices, teams can fully leverage source code management, enhancing collaboration, version control, and code backup. This fosters a more efficient and streamlined software development process.
Conclusion
In today’s software development landscape, source code management stands as an essential cornerstone. It is an integral aspect of software development, profoundly influencing the efficiency, reliability, and maintainability of a project.
The manner in which code is managed holds significant sway over the project’s success. Ineffectively managed source code can lead to time-consuming errors, project setbacks, and hindered collaboration. Conversely, a well-structured and meticulously documented source code can bolster productivity, teamwork, and the timely delivery of successful projects.
Hence, developers must prioritize source code management to ensure their objectives are met and to deliver top-notch software products of high quality and reliability.
Related Posts
Categories
- App Development (2)
- Design (2)
- DEVxHUB (30)
- Digital Marketing (2)
- Guide (24)
- It Bangladesh (1)
- Logo design (1)
- Operating system (1)
- Personal Improvement (14)
- Planning (4)
- Project management (3)
- Social media (2)
- Software Development (5)
- Software Quality Assurance (8)
- Startups (1)
- Team work (1)
- UI UX (1)
- Web Development (6)
Main Tags
- 2024
- Android
- app development
- bangladesh
- content writing
- design
- devxhub
- Digital marketing
- Guide
- IOS
- It
- logo design
- Operating system
- Personal Improvement
- planning
- project management
- social media
- Software Development
- Software Quality Assurance
- software testing
- software testing types
- Startups
- Success
- team
- UI UX
- UI UX design
- VR
- Web Development